Step by Step Video Guide to Reading Primary Sources
When we conduct research, need to explain changes in metrics or understand people'due south opinions, we e'er turn to qualitative data.
Qualitative data is typically generated through:
- Interview transcripts
- Surveys with open-ended questions
- Contact center transcripts
- Texts and documents
- Audio and video recordings
- Observational notes
Compared to quantitative data, which captures structured information, qualitative information is unstructured and has more depth. It tin answer our questions, can help codify hypotheses and build understanding.
But unfortunately, analyzing qualitative information is difficult. While tools similar Excel, Tableau and PowerBI crunch and visualize quantitative data with ease, there are no such mainstream tools for qualitative information. The majority of qualitative information analysis still happens manually.
That said, in that location are ii new trends that are changing this. First, there are advances in natural language processing (NLP) which is focused on understanding human language. Second, there is an explosion of user-friendly software designed for both researchers and businesses. Both help automate qualitative data analysis.
In this post nosotros desire to teach you how to deport a successful qualitative data analysis. We will teach you how to conduct the analysis manually, and also, automatically using software solutions powered by NLP.
Nosotros'll guide you through the steps to conduct a transmission analysis, and look at what is involved and the part technology can play in automating this process.
More than businesses are switching to fully-automated analysis of qualitative information because information technology is cheaper, faster, and just as accurate. Primarily, businesses buy subscriptions to feedback analytics platforms so that they can understand client hurting points and sentiment.

We'll take you through v steps to conduct a successful qualitative information assay. Within each step we volition highlight the cardinal divergence between the manual, and automated arroyo. Here's an overview of the steps:
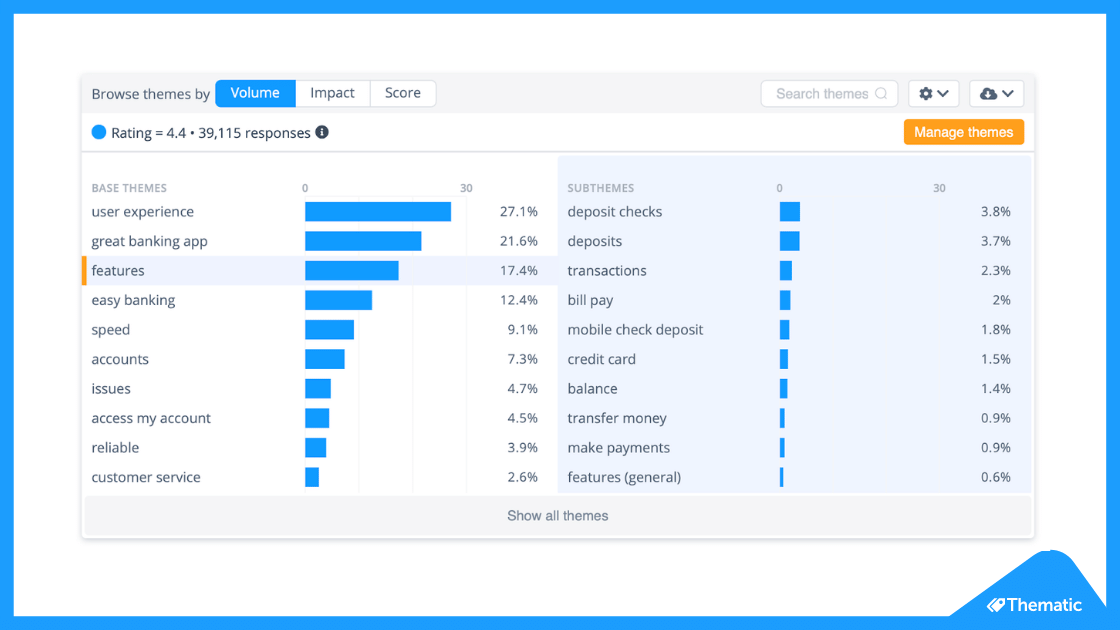
The 5 steps to doing qualitative data analysis
- Gathering and collecting your qualitative data
- Organizing and connecting into your qualitative data
- Coding your qualitative information
- Analyzing the qualitative information for insights
- Reporting on the insights derived from your assay
What is Qualitative Information Analysis?
Qualitative data analysis is a process of gathering, structuring and interpreting qualitative data to empathize what it represents.
Qualitative information is non-numerical and unstructured. Qualitative data generally refers to text, such as open-ended responses to survey questions or user interviews, but also includes sound, photos and video.
Businesses often perform qualitative information analysis on customer feedback. And inside this context, qualitative information generally refers to verbatim text information from sources such as reviews, complaints, chat messages, support middle interactions, customer interviews, example notes or social media comments.
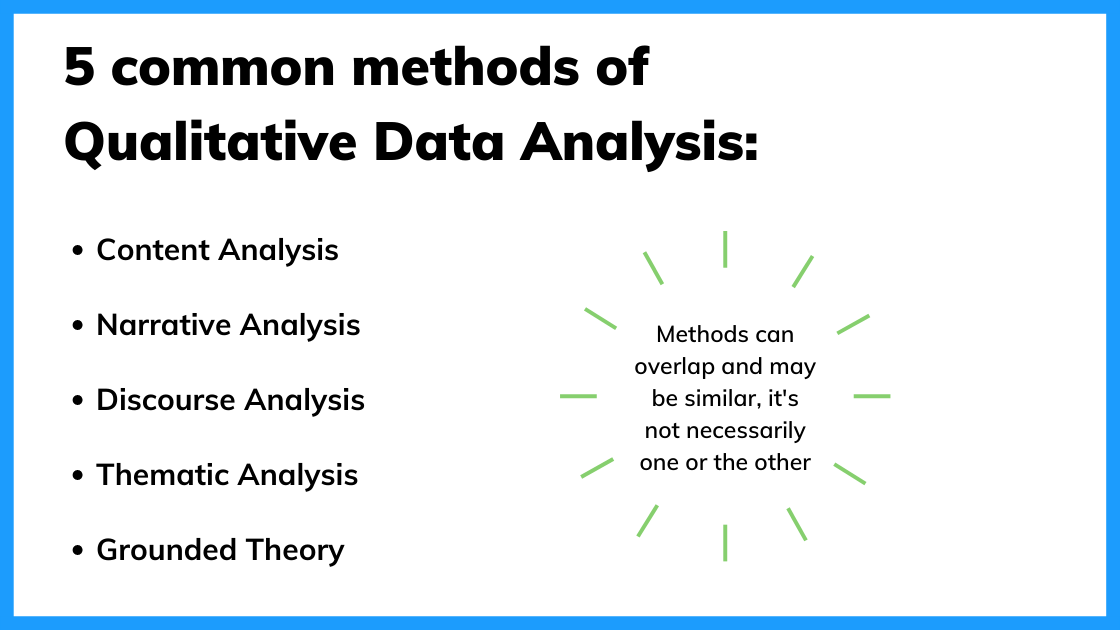
Qualitative Data Analysis methods
Once the data has been captured, in that location are a variety of analysis techniques available and the option is adamant by your specific research objectives and the kind of information you've gathered. Mutual approaches include:
Content Analysis
This is a popular arroyo to qualitative information analysis. Other analysis techniques may fit within the broad scope of content analysis. Thematic analysis is a part of the content analysis. Content analysis is used to identify the patterns that emerge from text, by grouping content into words, concepts, and themes. Content assay is useful to quantify the relationship between all of the grouped content. The Columbia Schoolhouse of Public Wellness has a detailed breakdown of content analysis.
Narrative Analysis
Narrative assay focuses on the stories people tell and the language they use to make sense of them. It is peculiarly useful for getting a deep understanding of customers' perspectives on a specific upshot. A narrative analysis might enable the states to summarize the outcomes of a focused case written report.
Discourse Assay
Discourse analysis is used to go a thorough understanding of the political, cultural and ability dynamics that be in specific situations. The focus here is on the way people limited themselves in different social contexts. Discourse analysis is ordinarily used by brand strategists who promise to sympathize why a group of people feel the way they do about a brand or product.
Thematic Analysis
Thematic assay is used to deduce the meaning behind the words people use. This is accomplished by discovering repeating themes in text. These meaningful themes reveal fundamental insights into data and tin can be quantified, particularly when paired with sentiment analysis. Often, the outcome of thematic analysis is a lawmaking frame that captures themes in terms of codes, too called categories. So the procedure of thematic analysis is likewise referred to as "coding". A common use-case for thematic assay in companies is analysis of client feedback.
Grounded Theory
Grounded theory is a useful approach when little is known virtually a subject. Grounded theory starts by formulating a theory around a single data case. This means that the theory is "grounded". It's based on actual information, and not entirely speculative. Then boosted cases can be examined to see if they are relevant and can add together to the original theory.
How to do Qualitative Data Assay: v steps
Now we are going to evidence how you can exercise your own qualitative data analysis. We volition guide you through this procedure step by step. As mentioned earlier, you volition learn how to practise qualitative information analysis manually, and besides automatically using modern qualitative data and thematic analysis software.
To get best value from the analysis process, it's important to be super articulate about the nature and telescopic of the question that's being researched. This will help y'all select the enquiry collection channels that are nearly likely to assist you answer your question.
Depending on if yous are a business concern looking to sympathize client sentiment, or an academic surveying a school, your approach to qualitative data analysis will be unique.
Once you lot're clear, there's a sequence to follow. And, though there are differences in the manual and automatic approaches, the process steps are by and large the same.
The use case for our step-by-pace guide is a visitor looking to clarify customer feedback - in order to improve customer experience. You lot can follow these aforementioned steps regardless of the nature of your inquiry. Permit's go started.
Pace one: Gather your qualitative information and bear research
The first step of qualitative research is to practise information collection. Put simply, data collection is gathering all of your data for analysis. A common situation is when qualitative information is spread across diverse sources.
Classic methods of gathering qualitative data
Most companies use traditional methods for gathering qualitative information: conducting interviews, running surveys, and running focus groups. This data is typically stored in documents, CRMs, databases and noesis bases. Information technology's important to examine which data is bachelor and needs to exist included in your inquiry, based on its scope.
Using your existing qualitative feedback
Every bit it becomes easier for customers to engage across a range of dissimilar channels, companies are gathering increasingly large amounts of both solicited and unsolicited qualitative feedback.
Most organizations have now invested in Voice of Client programs, back up ticketing systems, chatbot and support conversations, emails and even customer Slack chats.
These new channels provide companies with new ways of getting feedback, and besides let the collection of unstructured feedback data at scale.
The peachy thing nearly this information is that it contains a wealth of insights and that information technology'southward already there! When yous have a new question about your customers, you don't need to create a new research study or fix up a focus group. You lot can find most answers in the data you already have.
Typically, this data is stored in third-party solutions or a cardinal database, but there are means to export it or connect to a feedback analysis solution through integrations or an API.
Employ untapped qualitative data channels
There are many online qualitative data sources you may not have considered. For example, you can find useful qualitative information in social media channels similar Twitter or Facebook. Online forums, review sites, and online communities such as Discourse or Reddit also contain valuable information almost your customers, or research questions.
If you are considering performing a qualitative benchmark assay against competitors - the internet is your all-time friend. Gathering feedback in competitor reviews on sites like Trustpilot, G2, Capterra, Better Business Bureau or on app stores is a peachy way to perform a competitor benchmark analysis.
Customer feedback analysis software often has integrations into social media and review sites, or yous could apply a solution similar DataMiner to scrape the reviews.
Step two: Connect & organize all your qualitative information
Now yous all have this qualitative data but there's a trouble, the data is unstructured. Before feedback can be analyzed and assigned any value, it needs to exist organized in a unmarried identify. Why is this important? Consistency!
If all information is easily attainable in one place and analyzed in a consistent mode, y'all will have an easier fourth dimension summarizing and making decisions based on this data.
The transmission approach to organizing your information
The classic method of structuring qualitative information is to plot all the information you've gathered into a spreadsheet.
Typically, enquiry and support teams would share large Excel sheets and unlike business organization units would brand sense of the qualitative feedback information on their own. Each team collects and organizes the information in a way that best suits them, which means the feedback tends to be kept in separate silos.
An alternative and a more than robust solution is to store feedback in a primal database, like Snowflake or Amazon Redshift.
Keep in heed that when y'all organize your data in this way, y'all are often preparing it to be imported into another software. If you go the route of a database, you would need to use an API to push the feedback into a third-party software.
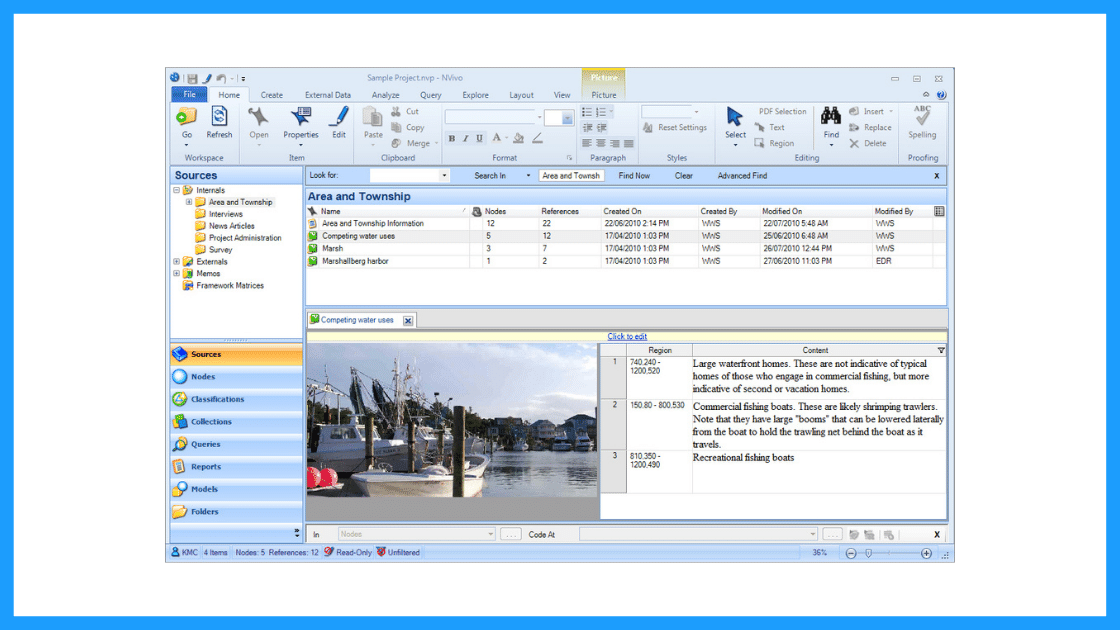
Reckoner-assisted qualitative data analysis software (CAQDAS)
Traditionally within the manual assay approach (but not always), qualitative information is imported into CAQDAS software for coding.
In the early on 2000s, CAQDAS software was popularised by developers such equally ATLAS.ti, NVivo and MAXQDA and eagerly adopted by researchers to assistance with the organizing and coding of data.
The benefits of using computer-assisted qualitative information analysis software:
- Assists in the organizing of your data
- Opens you up to exploring different interpretations of your data analysis
- Allows you to share your dataset easier and allows group collaboration (allows for secondary analysis)
However you still need to code the data, uncover the themes and do the analysis yourself. Therefore it is still a manual approach.
Organizing your qualitative data in a feedback repository
Some other solution to organizing your qualitative data is to upload it into a feedback repository where it tin can exist unified with your other data, and hands searchable and taggable. At that place are a number of software solutions that human activity as a central repository for your qualitative research data. Here are a couple solutions that you could investigate:
- Dovetail: Dovetail is a research repository with a focus on video and audio transcriptions. You can tag your transcriptions within the platform for theme analysis. You can also upload your other qualitative information such as research reports, survey responses, back up conversations, and customer interviews. Dovetail acts as a single, searchable repository. And makes information technology easier to collaborate with other people around your qualitative research.
- EnjoyHQ: EnjoyHQ is another enquiry repository with similar functionality to Dovetail. It boasts a more sophisticated search engine, only information technology has a higher starting subscription cost.
Organizing your qualitative data in a feedback analytics platform
If you have a lot of qualitative data and it is client or employee feedback, you will do good from a feedback analytics platform. A feedback analytics platform is a software that automates the process of both sentiment analysis and thematic analysis.
Companies apply the integrations offered past these platforms to directly tap into their qualitative data sources (review sites, social media, survey responses, etc.). The information is then organized and analyzed consistently within the platform.
If yous have data prepared in a spreadsheet, information technology can as well be imported into feedback analytics platforms.
Once all this information has been organized inside the feedback analytics platform, it is ready to be coded and themed, within the same platform.
Thematic is a feedback analytics platform that offers one of the largest libraries of integrations with qualitative data sources.
Step three: Coding your qualitative information
Your feedback data is now organized in i identify. Either inside your spreadsheet, CAQDAS, feedback repository or within your feedback analytics platform. The next step is to code your feedback data so we can extract meaningful insights in the next step.
Coding is the process of labelling and organizing your information in such a manner that you tin can and then identify themes in the information, and the relationships betwixt these themes.
To simplify the coding process, you will take small-scale samples of your customer feedback data, come up with a set up of codes, or categories capturing themes, and label each piece of feedback, systematically, for patterns and meaning. Then you volition take a larger sample of data, revising and refining the codes for greater accuracy and consistency as y'all go.
If you choose to use a feedback analytics platform, much of this process will be automatic and accomplished for you.
The terms to describe different categories of meaning ('theme', 'code', 'tag', 'category' etc) tin be confusing every bit they are often used interchangeably. For clarity, this commodity will utilize the term 'lawmaking'.
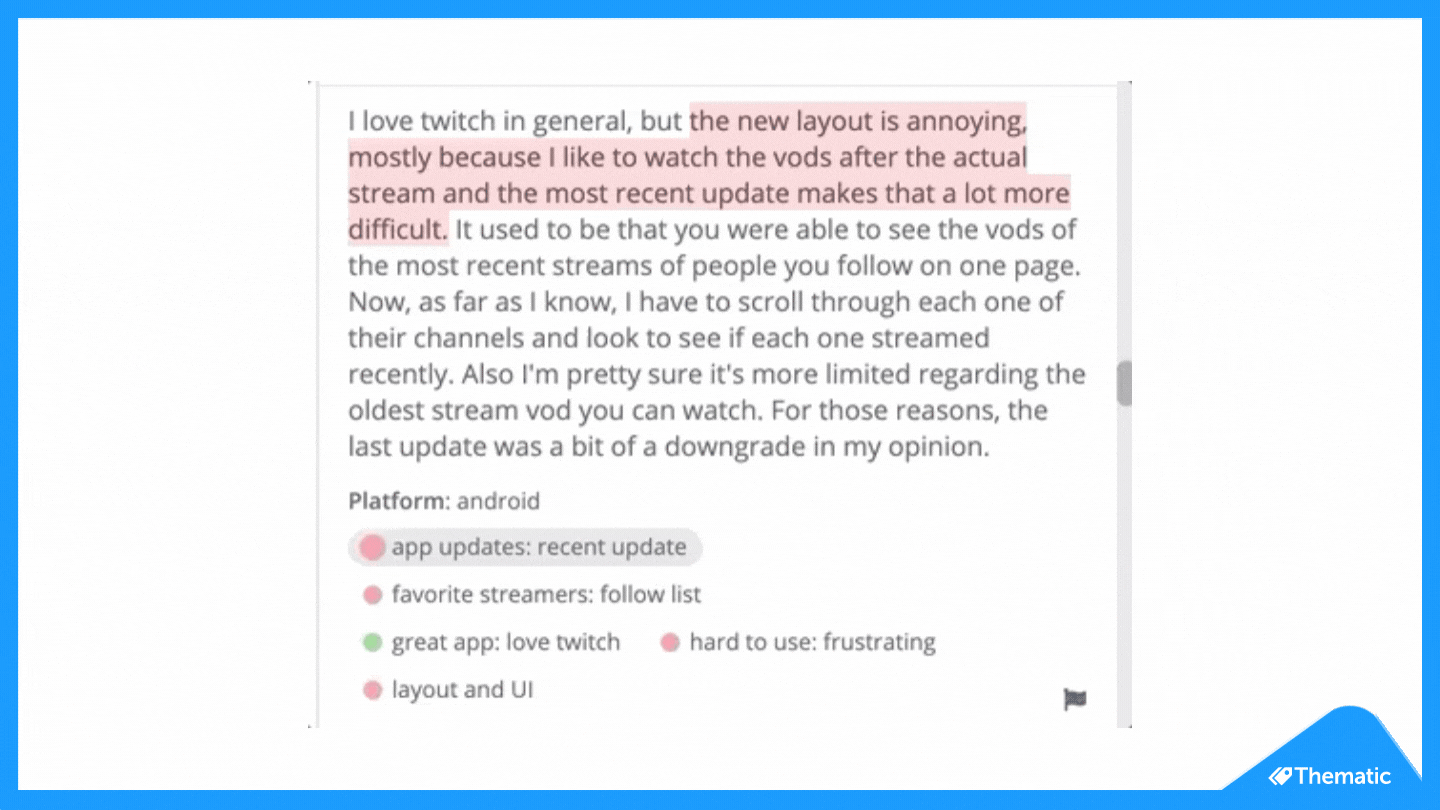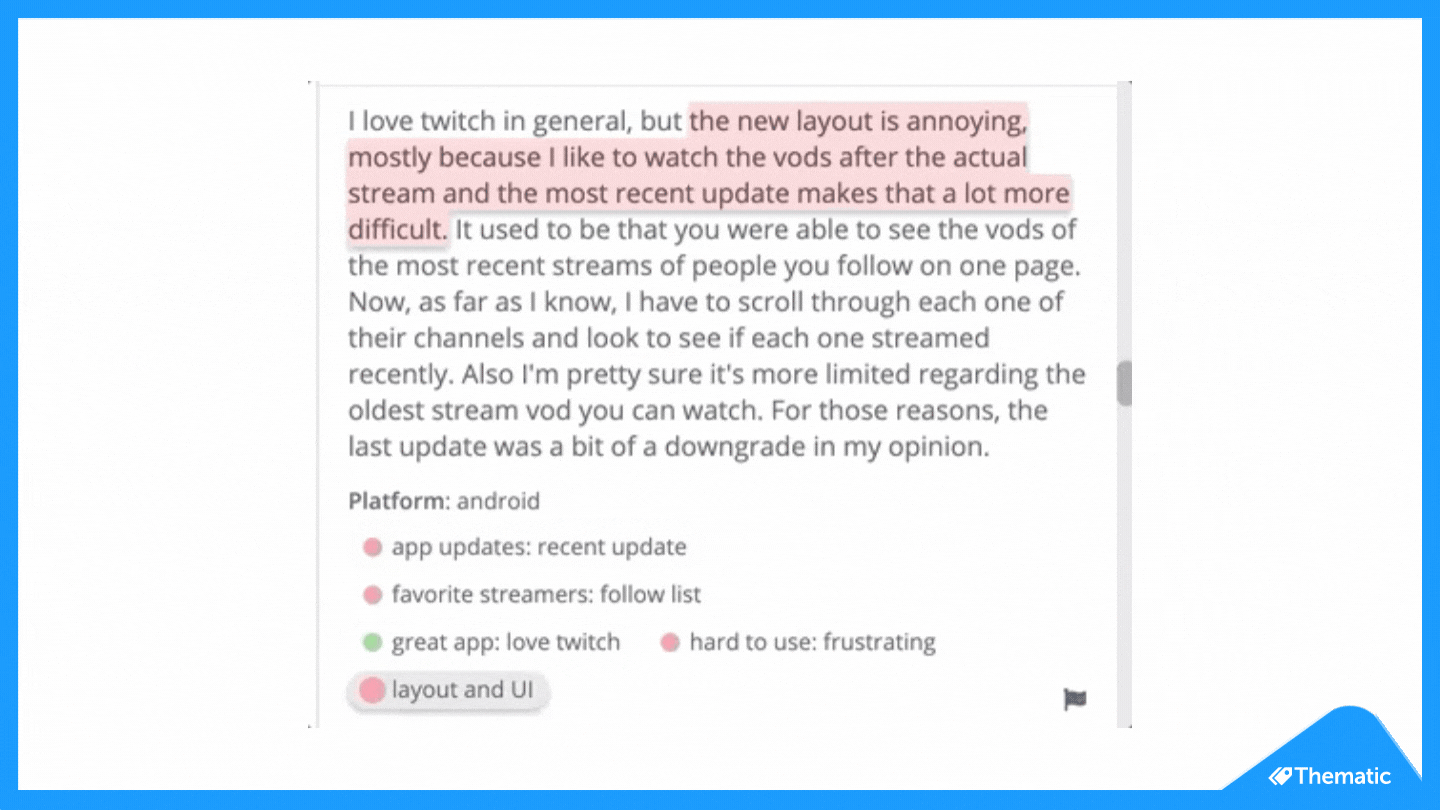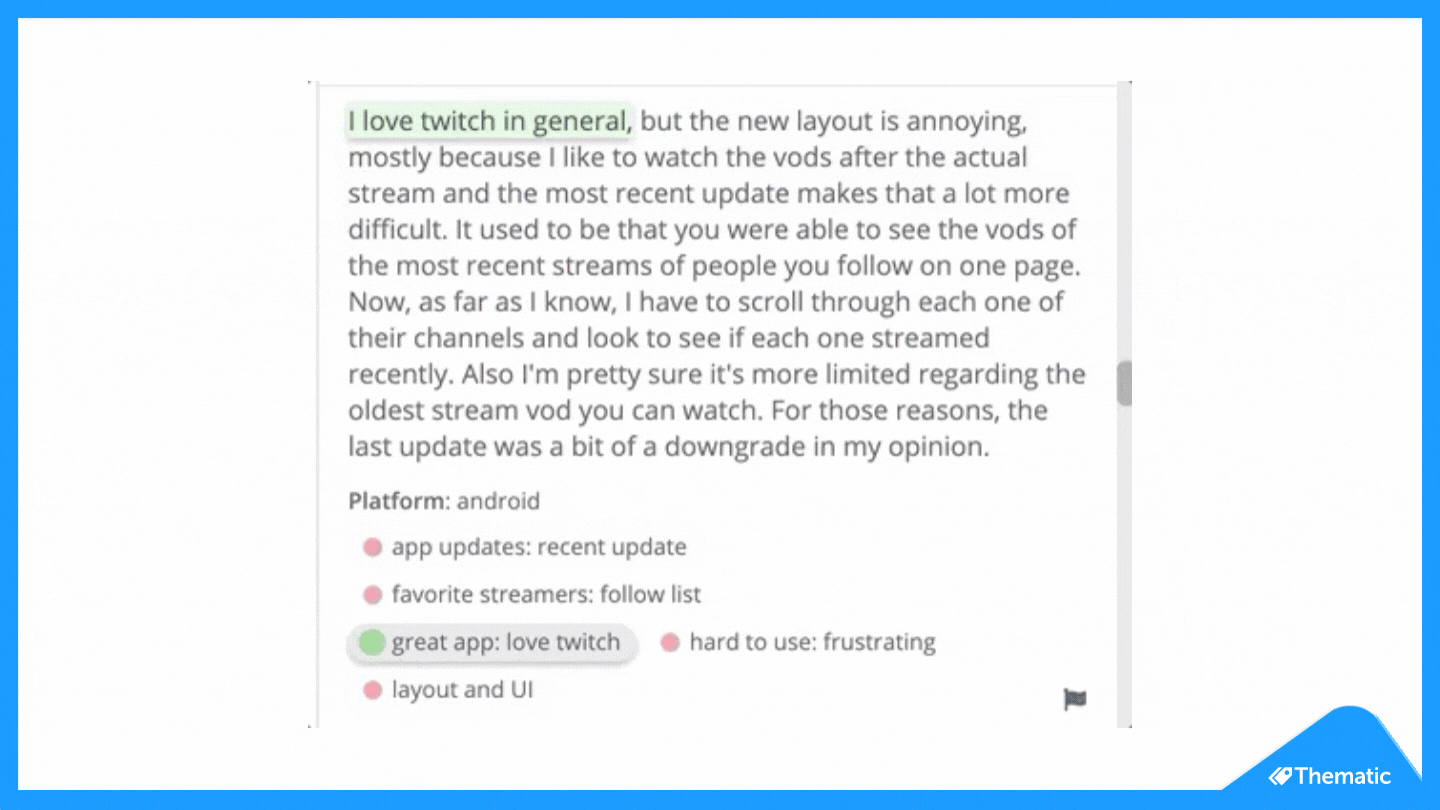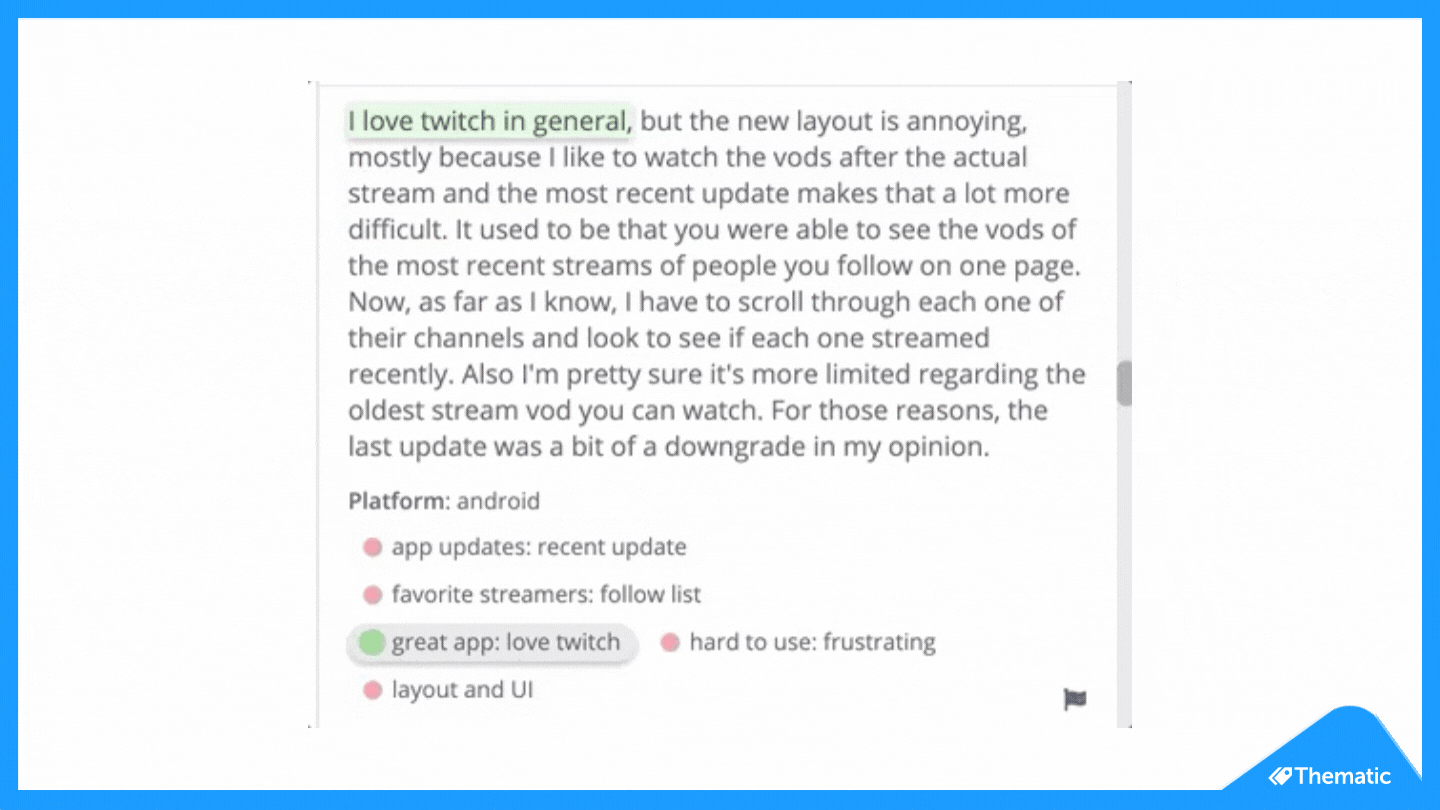
To code means to place central words or phrases and assign them to a category of meaning. "I really hate the customer service of this software company" would exist coded as "poor customer service".
How to manually code your qualitative information
- Decide whether you volition utilize deductive or inductive coding. Deductive coding is when yous create a listing of predefined codes, and and so assign them to the qualitative data. Anterior coding is the opposite of this, you create codes based on the information itself. Codes arise directly from the data and you label them as y'all get. You need to weigh upwardly the pros and cons of each coding method and select the most advisable.
- Read through the feedback data to get a wide sense of what it reveals. Now information technology's time to commencement assigning your first set of codes to statements and sections of text.
- Keep repeating footstep 2, adding new codes and revising the code description every bit often as necessary. Once it has all been coded, get through everything once more, to be sure at that place are no inconsistencies and that nothing has been overlooked.
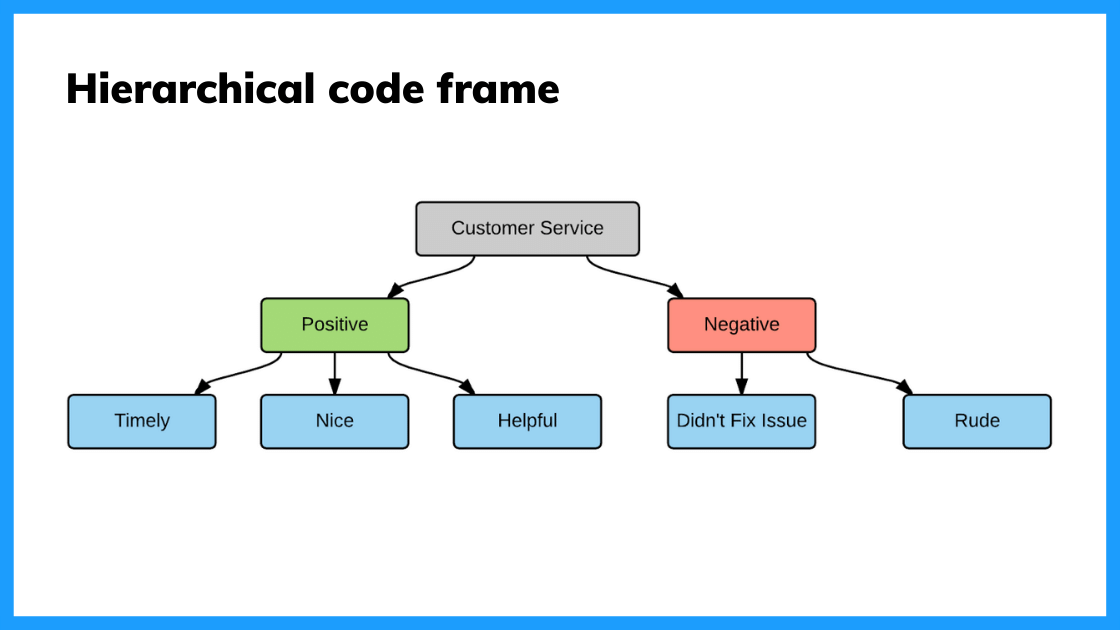
- Create a lawmaking frame to group your codes. The coding frame is the organizational structure of all your codes. And at that place are ii ordinarily used types of coding frames, flat, or hierarchical. A hierarchical code frame will make information technology easier for you to derive insights from your analysis.
- Based on the number of times a particular code occurs, you can now see the mutual themes in your feedback information. This is insightful! If 'bad customer service' is a common code, information technology's time to take action.
Nosotros have a detailed guide dedicated to manually coding your qualitative data.
Using software to speed upwards transmission coding of qualitative data
An Excel spreadsheet is still a pop method for coding. But diverse software solutions tin help speed up this process. Hither are some examples.
- CAQDAS / NVivo - CAQDAS software has built-in functionality that allows you to code text within their software. You lot may detect the interface the software offers easier for managing codes than a spreadsheet.
- Dovetail/EnjoyHQ - Yous can tag transcripts and other textual information within these solutions. As they are also repositories you may find it simpler to go on the coding in one platform.
- IBM SPSS - SPSS is a statistical analysis software that may brand coding easier than in a spreadsheet.
- Ascribe - Ascribe's 'Coder' is a coding management system. Its user interface volition make it easier for y'all to manage your codes.
Automating the qualitative coding process using thematic analysis software
In solutions which speed up the manual coding procedure, you however have to come up with valid codes and oft apply codes manually to pieces of feedback. But there are too solutions that automate both the discovery and the awarding of codes.
Advances in machine learning accept now made it possible to read, lawmaking and structure qualitative information automatically. This type of automated coding is offered by thematic analysis software.
Automation makes information technology far simpler and faster to code the feedback and group it into themes. By incorporating natural language processing (NLP) into the software, the AI looks across sentences and phrases to place meaningful statements.
Some automated solutions detect repeating patterns and assign codes to them, others make you railroad train the AI past providing examples. Y'all could say that the AI learns the meaning of the feedback on its own.
Thematic automates the coding of qualitative feedback regardless of source. In that location's no demand to set upwards themes or categories in accelerate. Simply upload your data and wait a few minutes. You can also manually edit the codes to further refine their accuracy. Experiments conducted indicate that Thematic's automated coding is just every bit accurate as manual coding.
Paired with sentiment analysis and advanced text analytics - these automated solutions become powerful for deriving quality concern or inquiry insights.
Y'all could also build your ain, if you lot have the resources!
The key benefits of using an automated coding solution
Automated analysis can ofttimes be set fast and there's the potential to uncover things that would never have been revealed if you had given the software a prescribed list of themes to look for.
Because the model applies a consistent dominion to the information, it captures phrases or statements that a homo heart might take missed.
Complete and consequent analysis of customer feedback enables more meaningful findings. Leading us into step iv.
Step 4: Analyze your information: Observe meaningful insights
At present nosotros are going to analyze our data to observe insights. This is where we beginning to answer our research questions. Keep in heed that step 4 and step 5 (tell the story) take some overlap. This is because creating visualizations is both role of analysis and reporting.
The task of uncovering insights is to scour through the codes that emerge from the data and draw meaningful correlations from them. Information technology is also about making sure each insight is distinct and has plenty data to support it.
Function of the analysis is to found how much each code relates to dissimilar demographics and customer profiles, and identify whether there's whatever relationship betwixt these data points.
Manually create sub-codes to better the quality of insights
If your code frame only has one level, you may find that your codes are too broad to be able to extract meaningful insights. This is where information technology is valuable to create sub-codes to your primary codes. This process is sometimes referred to as meta coding.
Note: If you take an inductive coding approach, you can create sub-codes every bit you are reading through your feedback data and coding information technology.
While time-consuming, this practise will meliorate the quality of your analysis. Here is an example of what sub-codes could look like.

You demand to carefully read your qualitative data to create quality sub-codes. Just equally y'all tin see, the depth of analysis is greatly improved. By calculating the frequency of these sub-codes y'all can get insight into which customer service problems you can immediately address.
Correlate the frequency of codes to client segments
Many businesses use customer segmentation. And you may take your own respondent segments that y'all can use to your qualitative analysis. Sectionalization is the practice of dividing customers or research respondents into subgroups.
Segments can be based on:
- Demographic
- Age
- Interests
- Behavior
- And any other data blazon that you intendance to segment by
It is specially useful to see the occurrence of codes within your segments. If one of your customer segments is considered unimportant to your business, but they are the cause of near all customer service complaints, it may exist in your best interest to focus attention elsewhere. This is a useful insight!
Manually visualizing coded qualitative information
There are formulas you can use to visualize key insights in your data. The formulas we will suggest are imperative if yous are measuring a score alongside your feedback.
Bear on
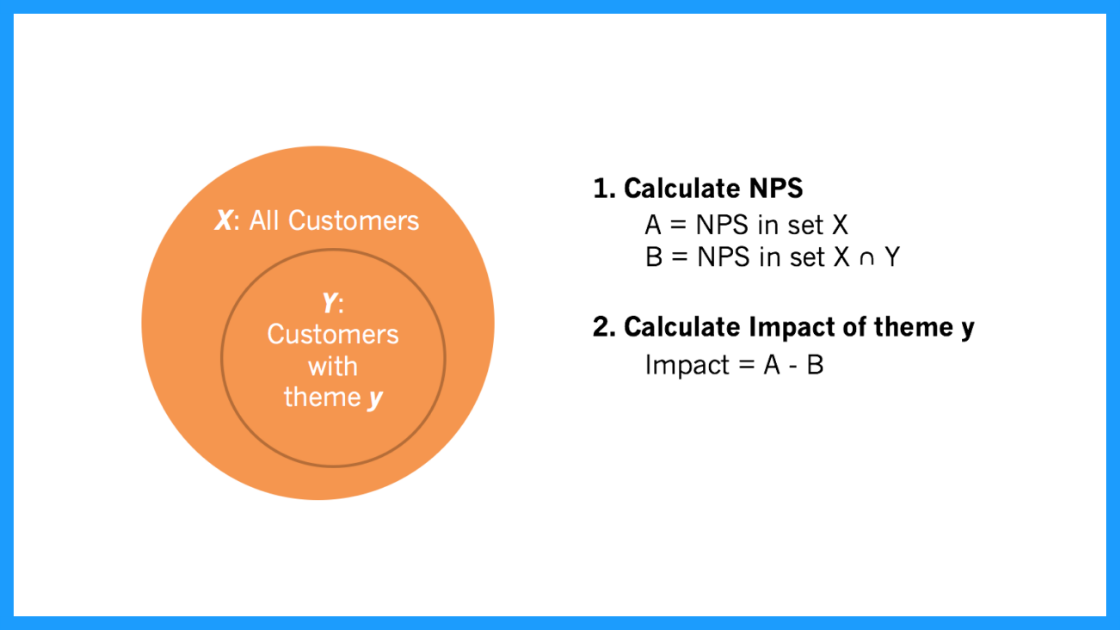
If you are collecting a metric alongside your qualitative information this is a key visualization. Impact answers the question: "What's the impact of a lawmaking on my overall score?".
Using Net Promoter Score (NPS) every bit an example, first you need to:
- Summate overall NPS
- Calculate NPS in the subset of responses that do not contain that theme
- Decrease B from A
Then you can utilize this simple formula to calculate code touch on on NPS.
Y'all can and so visualize this data using a bar chart.
You can download our CX toolkit - it includes a template to recreate this.
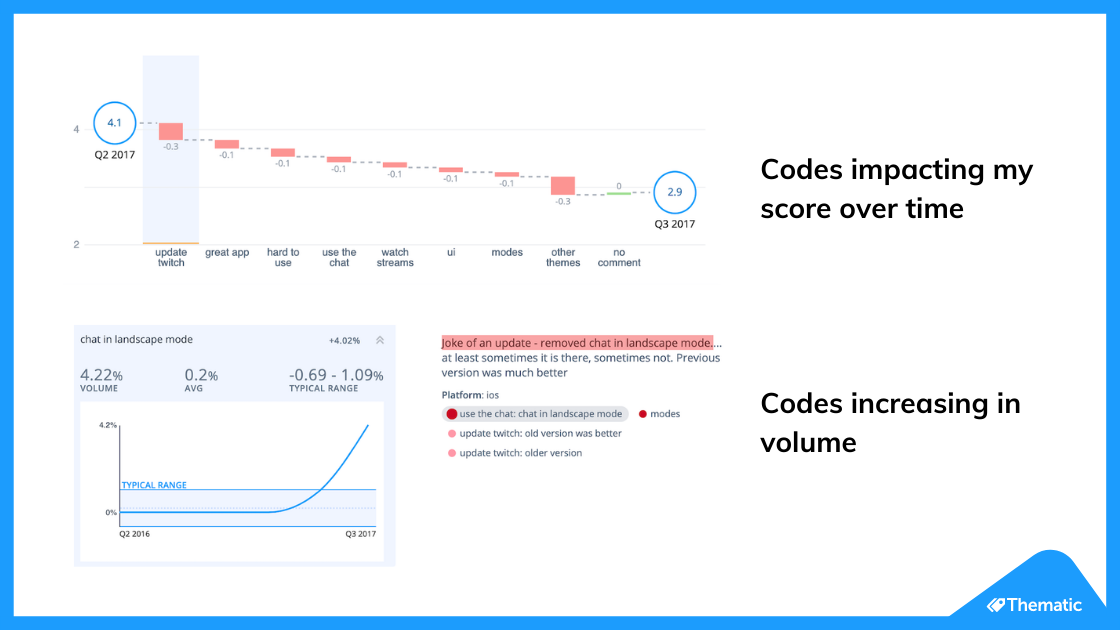
Trends over fourth dimension
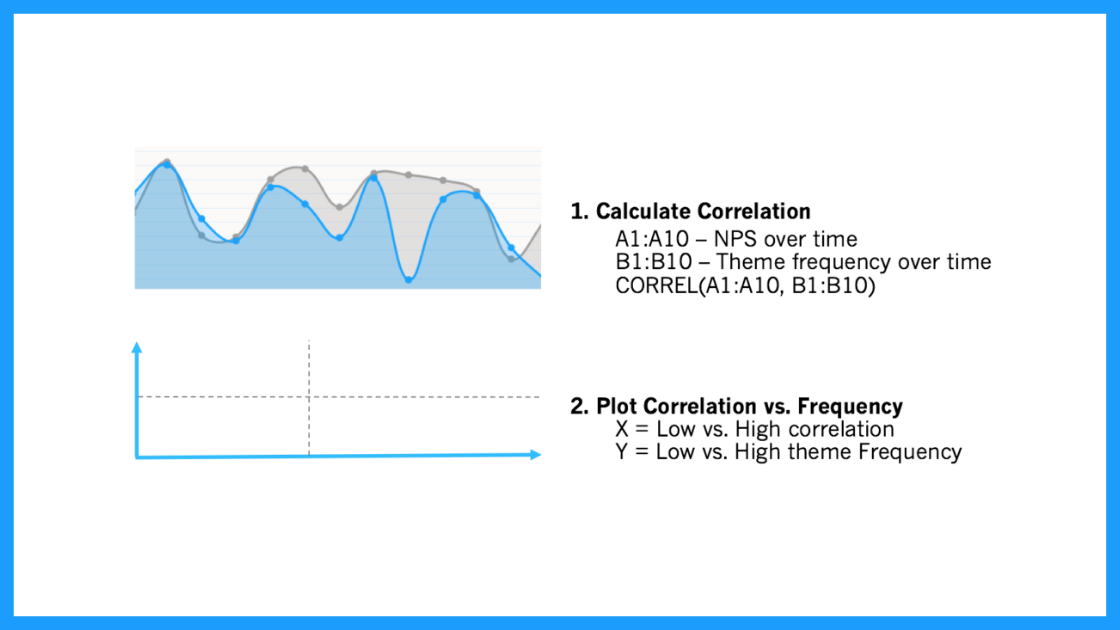
This analysis can help you answer questions like: "Which codes are linked to decreases or increases in my score over time?"
Nosotros need to compare two sequences of numbers: NPS over time and lawmaking frequency over time. Using Excel, summate the correlation between the two sequences, which can exist either positive (the more codes the higher the NPS, see picture below), or negative (the more codes the lower the NPS).
Now you lot need to plot code frequency against the absolute value of code correlation with NPS.
Hither is the formula:
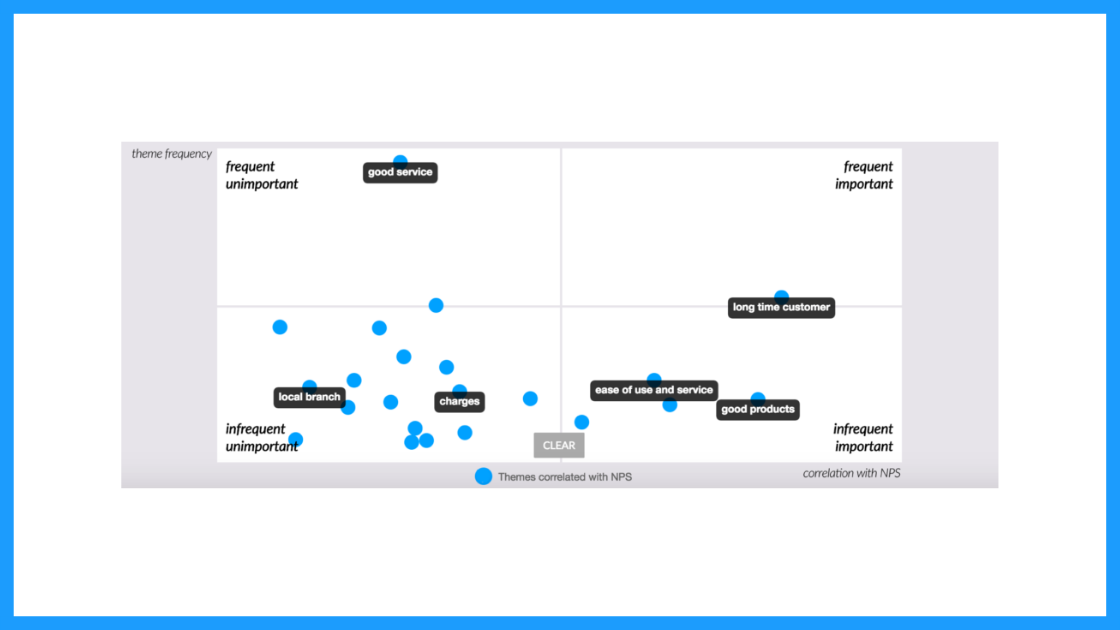
The visualization could look like this:
These are two examples, merely there are more than. For a third manual formula, and to learn why discussion clouds are not an insightful form of analysis, read our visualizations article.
Using a text analytics solution to automate assay
Automatic text analytics solutions enable codes and sub-codes to exist pulled out of the data automatically. This makes it far faster and easier to place what's driving negative or positive results. And to pick up emerging trends and detect all fashion of rich insights in the data.
Another benefit of AI-driven text analytics software is its built-in capability for sentiment assay, which provides the emotive context behind your feedback and other qualitative information.
Thematic provides text analytics that goes further past allowing users to apply their expertise on business context to edit or broaden the AI-generated outputs.
Since the move away from manual research is generally about reducing the human element, calculation human input to the technology might sound counter-intuitive. Withal, this is generally to make sure important business nuances in the feedback aren't missed during coding. The result is a higher accurateness of analysis. This is sometimes referred to every bit augmented intelligence.
Step v: Report on your data: Tell the story
The last footstep of analyzing your qualitative information is to report on it, to tell the story. At this betoken, the codes are fully developed and the focus is on communicating the narrative to the audience.
A coherent outline of the qualitative research, the findings and the insights is vital for stakeholders to discuss and fence before they tin can devise a meaningful class of activity.
Creating graphs and reporting in Powerpoint
Typically, qualitative researchers take the tried and tested approach of distilling their report into a serial of charts, tables and other visuals which are woven into a narrative for presentation in Powerpoint.
Using visualization software for reporting
With information transformation and APIs, the analyzed data tin can exist shared with information visualisation software, such every bit Power BI or Tableau, Google Studio or Looker. Power BI and Tableau are among the most preferred options.
Visualizing your insights inside a feedback analytics platform
Feedback analytics platforms, like Thematic, incorporate visualisation tools that intuitively plough key information and insights into graphs. This removes the time consuming work of constructing charts to visually identify patterns and creates more fourth dimension to focus on building a compelling narrative that highlights the insights, in bite-size chunks, for executive teams to review.
Using a feedback analytics platform with visualization tools means you don't have to apply a separate product for visualizations. You tin export graphs into Powerpoints straight from the platforms.
Conclusion - Transmission or Automated?
There are those who remain securely invested in the transmission approach - because it'southward familiar, because they're reluctant to spend money and fourth dimension learning new software, or because they've been burned by the overpromises of AI.
For projects that involve modest datasets, manual assay makes sense. For instance, if the objective is simply to quantify a simple question like "Do customers prefer X concepts to Y?". If the findings are being extracted from a modest prepare of focus groups and interviews, sometimes it'southward easier to simply read them
However, as new generations come into the workplace, it'due south technology-driven solutions that feel more comfortable and applied. And the merits are undeniable. Particularly if the objective is to go deeper and sympathise the 'why' behind customers' preference for 10 or Y. And fifty-fifty more specially if time and coin are considerations.
The power to collect a gratis flow of qualitative feedback data at the same time every bit the metric ways AI can toll-finer scan, crunch, score and analyze a ton of feedback from one organization in one go. And time-intensive processes similar focus groups, or coding, that used to take weeks, can at present be completed in a matter of hours or days.
But bated from the ever-present business case to speed things upward and keep costs down, there are also powerful research imperatives for automated analysis of qualitative data: namely, accuracy and consistency.
Finding insights hidden in feedback requires consistency, especially in coding. Not to mention catching all the 'unknown unknowns' that can skew research findings and steering clear of cerebral bias.
Some say without manual information assay researchers won't become an accurate "feel" for the insights. However, the larger data sets are, the harder it is to sort through the feedback and organize feedback that has been pulled from different places. And, the more hard it is to stay on grade, the greater the run a risk of cartoon incorrect, or incomplete, conclusions grows.
Though the process steps for qualitative data analysis accept remained pretty much unchanged since psychologist Paul Felix Lazarsfeld paved the path a hundred years ago, the impact digital technology has had on types of qualitative feedback data and the approach to the analysis are profound.
If you want to try an automated feedback assay solution on your own qualitative data, you tin get started with Thematic.
Source: https://getthematic.com/insights/qualitative-data-analysis/
0 Response to "Step by Step Video Guide to Reading Primary Sources"
Enregistrer un commentaire